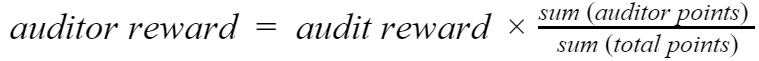Previous audits can be found here: https://github.com/CallistoSecurity/AuditReports/tree/main/Reports
In our continuous efforts to enhance the value of CLO, we are introducing a strategic initiative that links the Callisto Security Department's activities directly with the value of CLO. A portion of the revenue from our audit services, equivalent to 20%, will be used to buy back CLO tokens and burn them. This unique approach aligns the success of our audit services with the prosperity of the CLO ecosystem, reinforcing our commitment to maintaining the most affordable audits in the market while simultaneously supporting the CLO value.
There are three options of the security audit workflow suitable for small-, medium- and large-scale projects:
- Standard (standard projects such as ICOs, ERC20, ERC223, ERC721, ERC721A tokens, and NFTs fall in this category - 2 auditors. $600 + $1.2 per line of code / minimum $1200)
- Advanced (non-standard projects requiring more careful review - 3 auditors. $1200 + $1.5 per line / minimum $2400)
- Corporate (projects that require post-launch support - 3 auditors - Callisto Team will handle the bug-bounty and provide a 1-month long period of technical support regarding the necessary security enhancement procedures and track/highlight any issues and potential threats - this plan allows to further apply for Callisto DAPP Insurance program)
Audit request can be submitted directly via Github Issues or open telegram channel :
- Go to the Auditing/issues section and click a New Issue button.
- Fill out the form and click the "Submit New Issue" button.
- Follow the comments in the corresponding "issue" discussion.
- The result of a security audit will be published in the comment thread with the
Security Audit Reportheader once auditors complete their tasks.
Although we provide free audits, we ask our customers to understand that real people work in our organization, not automated tests. We strongly recommend using specifically designed tools for debugging and testing. We also recommend using automated tests to verify minor changes and fixes.
Please, only submit your code for review once the smart-contract development is in its final stage, and the contract is ready for deployment.
Re-auditing a smart contract includes a full check of the smart-contract code, as any minor changes could affect the overall behavior of the smart contract. Even if 10 lines of code were changed, the entire smart contract would be re-audited.
There are two ways to avoid a complete re-audit if the contract is updated:
-
break your smart contract into modules so that they can be audited separately from each other
-
cover the smart-contract code with automated tests to prove that the update did not affect the behavior of the smart-contract
Callisto Security accept USDT tokens on ETH or BSC chain to the multisig wallet address 0x6317c6944bd1cD3932d062cce39d7Fd602119529
There are two types of participants in the Security Department:
- auditing manager
- security auditors
For smart contracts, the following order of audits is determined:
- Important contracts for the whole cryptocurrency industry can have the highest priority.
- Contracts intended for deployment in the CLO network have the highest priority (except for the previous paragraph).
- Contracts of the ETH network have medium priority.
- Other contracts have low priority.
- If the audit of the smart contract is already started, then it continues until it is completed, regardless of the availability of other contracts with higher priority in the queue.
After the audit request has been created, it is viewed by the audit manager. If the request meets the requirements, the auditing manager assigns it approved status. approved label means that the audit request is available for auditors to pick.
If there are several requests with different priorities in the queue, then the manager should assign the approved status only to contracts with the highest priority. The remaining contracts will be checked after the audit of the contracts with the highest priority has been performed. If several contracts are in the queue with the highest priority, then the audit manager should assign the status of approved to all these contracts simultaneously. In this case, the contract that auditors will begin to check first will be checked earlier.
Audit requests that remained in "awaiting payment" status for more than two weeks must be closed.
After an audit request with an approved label appears, an auditor can pick it by commenting on the issue and indicating how long it should take to audit this smart contract (roughly/ in days). After that, the auditor can start reviewing the code immediately. Other community members may also pick the request and submit their audit reports. These reports must be reviewed by the auditor manager at the end of the auditing process. If the audit request was approved, but none of the auditors picked it, then the audit manager can appoint auditors to check this request if they are not engaged in checking another smart contract.
The auditing manager must comment that the audit is successfully started and mention the GitHub nicknames of all the auditors responsible for checking the corresponding contract after several auditors have picked the issue request. The audit manager must also comment on his contact email, to which the auditors will send their secret gists (audit reports).
After the auditor began to check the code, he must create a secret github gist and send it to the auditing manager by email. An auditor must not reveal the audit report gist or publish it anywhere so that only the auditing manager and auditor (gist owner) can review it during the auditing process.
After the auditor has completed the code verification, he should comment on the appropriate issue that his audit report is completed. NOTE: An auditor must not reveal his report gist!
The Security Auditing Manager can participate in the audit process alongside assigned auditors. In this case, he should create his own Audit Report gist as if he was an auditor and perform the review of the contract code. Since the manager sees all the auditors' reports in the process, he should only describe those findings that the other auditors failed to report.
The Security Auditing Manager is not obligated to participate in the auditing process.
There are two possible scenarios for rewarding Security Auditors and Auditing Managers:
- In case the Auditing Manager found any "medium" or higher severity issues that other auditors failed to report, then these "medium" severity issues must be used in the reward calculation formula (see Auditing Department reward calculation v2). The auditing Manager is paid for the finding of this issue upon completing the audit as if he was an active auditor.
- In case the Auditing Manager did not find any "medium" or higher severity issues that other auditors failed to report, then the Auditing Manager is excluded from the process of reward calculation.
After all the responsible auditors have completed their reports, the audit manager must compare them.
If there are no significant discrepancies in the reports and no critical errors were found, then the audit manager must complete the audit by summarizing the reports and submitting secret gist URLs in the comment thread of the corresponding audit request issue. The audit is considered complete after all the responsible auditors have submitted their reports, and the audit manager has summarized the results of these reports and published report gist URLs.
If one of the community members has expressed a desire to participate in the audit of this contract and also sent his report to the audit manager, then the audit manager must review the report and comment its secret gist URL to the corresponding GitHub request-issue regardless of whether the audit was already completed or not.
If any of the auditors described findings that were not included in the final report, then the auditing manager must describe the reason for excluding these findings in the comment thread of his fork of the auditor's report-gist.
Read more here: Standard disclosure policy of Callisto
After completing the audit, the audit manager may inform the customer about the results without revealing the reports. After 15 days from informing the customer about the findings, the reports should still be published and the results summed up.
Security auditors are paid based on the results of their work. Depending on the payment scheme for audit requests (free auditing campaign or paid audit), the auditor's salary is calculated using the methods described below.
In the Security Department of Callisto, smart-contract auditors are paid once a month.
The total payment amount is calculated based on the number of tasks performed last month. Each security audit is evaluated separately and a security auditor receives payment for each audit.
Each finding has a certain weight in points. The following values will be used to evaluate findings according to its severity:
| Severity | Weight in points |
|---|---|
| Critical | 100 |
| High | 45 |
| Medium | 8 |
| Owner privileges | 2 |
| Low/Note | 1 |
The following formula is used to calculate the auditor's reward for the assigned task:
Where:
reward - the amount of CLO that will be paid to the auditor for his(her) contribution to this security audit.
audit reward = budget for this audit.
sum (auditor points) - all points the auditor earns.
sum (total points) - the sum of all points earned by each auditor individually.
The [number of lines] of code in the source code of the auditable smart contract is calculated excluding empty lines and comments. SLOC Counter will be used for this purpose.
Auditors will receive the reward depending on the quality and quantity of the work done. If a contract has only low-severity issues or no issues, then its reward will be divided equally between all auditors who worked on the security audit of this contract.
The main task of each security auditor is to check the code for security-related mistakes and write a report on the detected errors after the audit is completed.
- All the work will be coordinated through GitHub. Each auditor must visit the Auditing/issues repository section every (working) day.
If an audit request (issue) labeled approved appears in the list, the auditor may pick it. The audit manager can appoint an auditor if he is not engaged in smart contract checking by mentioning their GitHub nicknames in the corresponding issue. If the auditor was appointed to a certain issue by the auditing manager, then the auditor must verify the corresponding contract.
-
After the auditor has received the objective of his work, he must comment on the time that, in his opinion, will be required to verify this smart contract.
-
The auditor must create a secret gist (audit report template) and send it to the auditing manager by email. WARNING: the auditor must never reveal the gist URL. The auditing manager will reveal it at the end of the auditing process. The secret gist should be named as follows:
NETWORK_contract_name_report.md
Example: ETH_the_dao_report.md
- The auditor must check the contract code, perform necessary testing and describe findings at the secret gist (audit report).
Other auditors, community members, and the audit manager will also check this smart contract, so the auditor is not incentivized to hide the errors found or try to exploit them.
- After the auditor has completed the code verification and supplemented his report with a description of the findings, he should comment on the issue that his report is finished.
The audit report name should start with a capital letter. Use underscores instead of spaces between words, and write reports in .md format.
The report should contain a title describing to which contract or contract system the report belongs.
The report should contain the following sections:
Briefly describe the audit report, the purpose of a contract (or contract system) that was reviewed, and key features of the contract.
This may be important to understand the inner logic of the contract or a contract system.
Specify the range of contracts and the version of the contracts that have been verified. If the source code was published on Github, specify the commit hash.
Specify which files or contracts were not checked during the audit and if there were any contracts/files that were excluded for some reason.
Summarize the total amount of mistakes and their severity.
Describe each bug/mistake/error separately
Severity assigning:
-
high - vulnerability can be exploited at any time and cause a loss of customers' funds or a complete breach of contract operability. (Example: Parity Multisig hack, a user has exploited a vulnerability and violated the operability of the whole system of smart-contracts (Parity Multisigs). This could be performed regardless of external conditions at any time.)
-
medium - vulnerability can be exploited in some specific circumstances and cause a loss of customers' funds or a breach of operability of a smart contract (or smart-contract system).
-
low - vulnerability can not cause a loss of customers' funds or a breach of contract operability. However, it can cause problems or inconveniences. (Example: Permanent owners of multisig contracts, owners are permanent, thus if it will be necessary to remove a misbehaving "owner" from the owners list then it will require to redeploy the whole contract and transfer funds to a new one.)
-
minor observation - other code flaws, not security-related issues.
-
owner privileges - a specific severity class for findings that provide the owner with the ability to manipulate the contract in such a way that it could theoretically harm users in case the owner acts maliciously, or the owner's account gets compromised.
Give a link to a code fragment that can lead to an error you describe.
Describe this finding in detail.
Write down how the bug can be fixed if you know how to do it. However, fixing bugs is not the primary goal of the security auditor.
Describe the most important findings and their relationship to the main purpose of the contract. Describe how the internal logic of the contract is related to its purpose. Indicate whether the contract is safe or whether any critical problems must be resolved.
https://gist.github.com/yuriy77k/3d37730343d51b6113543cd8c3d366e4