This is a simple repository that aims to have the bare minimal example to use and compile the PortAudio library on Windows 8.1 / Windows 10 using the WMME audio interface and produce some noise with the library to the default audio device.
To compile this you need to have installed Windows Visual Studio 2019, because the compiling script will try to use the following compiling enviroment:
C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\Community\VC\Auxiliary\Build\vcvars64.bat
The steps to compile this are:
- Download (and extract) this repository
- Run
compile-windows-loop.bat
This should compile the main.c file and every relevant portaudio source file and then run your executable.
Your executable should output 5 seconds of constant tone at 220.5 Hz at the default output audio device at 25% of the current volume.
If you press any key it will attempt to compile and run again. The main.exe will be left at the root of the project for you to use. There's no develolpment or production enviroment, everything is done in production enviroment.
After compiling the program with the batch script you should have an exe that outputs a senuidal wave audio to the default audio device for 5 seconds. The sampling frequency is set to 44100 Hz.
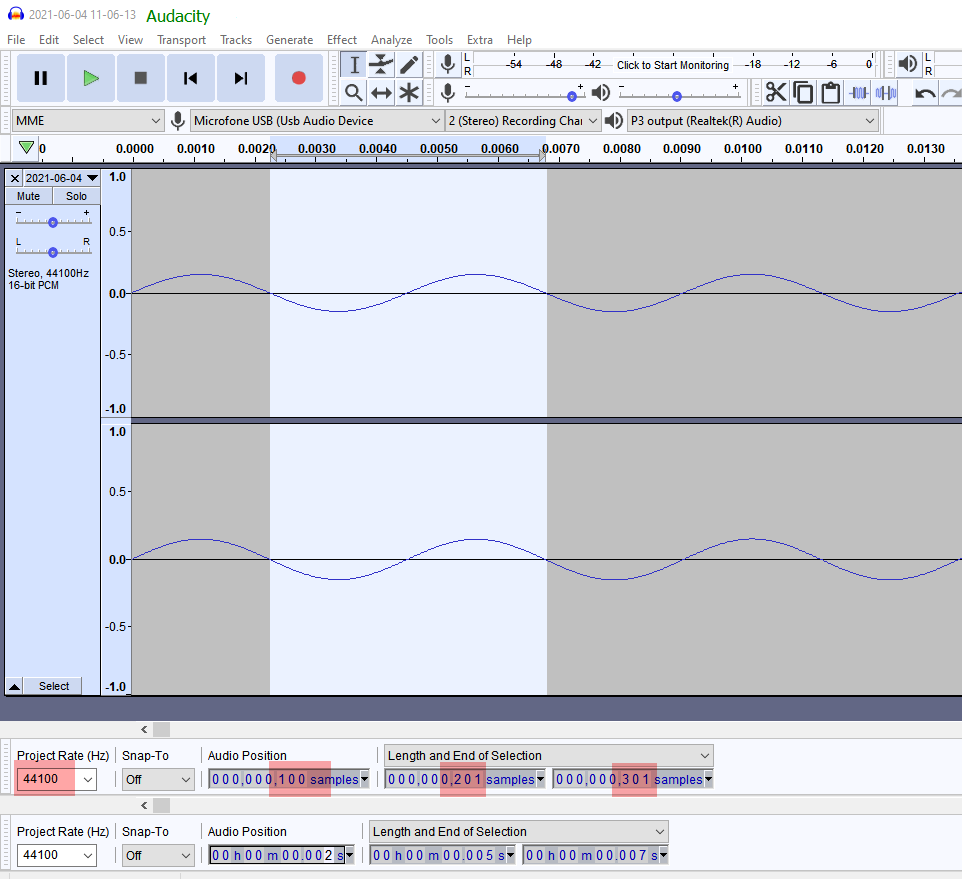
Its attenuated to 25% of the full audio amplitude (equivalent to -16 dB). Here's the output wave analysis from audacity:
As you can see it repeats every 200 frames (the size of the sinuidal buffer) in the specified sampling frequency (44.1k), which should yield 44100/200 = 220,. Hz. Using this generator I managed to check that yes, the program is generating exactly 220.5 Hz.
The library used here (PortAudio) is the dependency of a lot of audio transforming tools in the market (except really expensive ones), so by getting it to compile and use its interface we can simulate any other audio processing, such as:
- Creating programs that output audio to specific devices (or default) from files
- Analyse wav files content in a raw format
- Reroute audio between input devices and output devices
- Transforming audio with a mathematical implementation that runs on native hardware
Moreover, you can use the default PortAudio documentation to manipulate audio, which might be better than your operational system documentation: http://www.portaudio.com/docs.html
There are some releases for basic versions that were not fully working if you need other executables or source code, in case something goes wrong you might need to use old versions to debug better as they have some debugging included on them.
The PortAudio library was not made by me, it is being included at a subfolder because otherwise this wouldn't compile. The PortAudio license is found at ./portaudio\LICENSE.txt