This database keeps track of the medical staff of a dental clinic, as well as the patients and all the medical processes performed in the clinic daily.
Within the scope are:
- Doctors. In addition to data that identifies each one, we can find recorded the dates on which they began to work at the clinic and - if applicable - the date of completion of the work relationships.
- Patients. Data that identifies them individually.
- Assistants. Identification data, start dates of work within the clinic, and - if applicable - end date of the employment relationship.
- Treatments. Catalog of treatments offered within the clinic for patients.
- Appointments. Record of appointments scheduled by patients. Includes identification of the patient and identification of the doctor who will attend him/her.
- Daily entries. Here you can find details of each treatment performed on each patient within the clinic.
This database does not include information on administrative staff or financial data related to the clinic.
Users of this database will be able to:
- Record and consult the medical processes carried out daily within the dental clinic.
- Consult start and end dates of work relationships between the clinic and the medical staff.
- Record and consult patients' appointments.
The entry or consultation of financial information is not possible in this database.
This database was made in sqlite following this schema.
id,primary keyof this table of typeINTEGER. It indicates the unique ID of each doctor.first_name, represents the first name of each doctor asTEXT. The values in this column are required so theNOT NULLconstraint is applied.last_name, represents the last name of each doctor asTEXT. The values in this column are required so theNOT NULLconstraint is applied.specialization, representing the specific area of dentistry in which each doctor specializes, is stored asTEXT. The values in this column are required so theNOT NULLconstraint is applied. In addition, theCHECKconstraint is also applied to limit the specialization options to: general dentist, pediatric dentist, orthodontist, periodontist, endodontist, oral pathologist, oral surgeon, prosthodontist.start_date, indicates the date when each doctor started working in the clinic, it is stored with the affinity typeNUMERIC. This value is required so theNOT NULLconstraint is applied.end_date, in the case that the doctor and the clinic have ceased their work relationship, this column will store the date when the relationship ended. It is stored with the typeNUMERICand in the case of not saving any data the value for DEFAULT will beNULL.
id,primary keyof this table of typeINTEGER. It indicates the unique ID of each patient.first_name, indicates the first name of each patient asTEXT.last_name, indicates the last name of each patient asTEXT.birth_date, indicates the patient's date of birth, stored with the affinity typeNUMERIC.registration_date, indicates the date on which the patient scheduled his or her first appointment. It is stored with typeNUMERICand the default value isCURRENT_TIMESTAMP.
The values of each column in this table are required so the NOT NULL constraint applies to all columns.
This table contains information about the dental assistants working in the clinic.
id,primary keyof this table of typeINTEGER. It indicates the unique ID of each assistant.first_name, indicates the first name of each assistant asTEXT.last_name, indicates the last name of each assistant asTEXT.birth_date, records the date of birth of each dental assistant, stored asNUMERIC.start_date, records the date when each assistant started working with the clinic. It is stored with typeNUMERIC.end_date, if applicable, indicates the date of the end of the working relationship between the clinic and the assistant, with typeNUMERIC.
All columns except end_date require a value so the NOT NULL constraint applies.
id,primary keyof this table asINTEGER. Represents the unique ID for each treatment available in the clinic's options catalog.name, represents the specific name of the treatment, it is of typeTEXT.dental_specialty, indicates the dental specialization to which the type of treatment belongs, it is of typeTEXT.
Both name and dental_specialty require a value to be specified so the NOT NULL constraint is applied.
id,primary keyof this table asINTEGER. It uniquely identifies each appointment scheduled in the clinic.date_app_was_made, indicates the date in which the appointment was registered. It is of typeNUMERIC, this information is required so theNOT NULLconstraint is applied and the DEFAULT value is CURRENT_TIMESTAMP.appointment_date, indicates the date for which the appointment was made, of typeNUMERIC, and is required information so theNOT NULLconstraint is applied.patient_id, specifies the ID of the patient who will be seen on the date indicated inappointment_date. It refers to theidcolumn of thepatientstable, so theforeign keyconstraint is applied.doctor_id, indicates the ID of the doctor responsible for treating the patient on the date indicated inappointment_date. It refers to theidcolumn of thedoctorstable so theforeign keyconstraint is applied.
This table records the details of each clinical process that happens daily within the clinic, specifying the people and treatments involved.
id, represents the unique ID for each entry, it is theprimary keyof this table, of typeINTEGER.datetime, indicates the date on which the entry is registered. This value is necessary so theNOT NULLconstraint is applied being the value ofDEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP. It is of theNUMERICtype.patient_id, indicates the ID of the patient that was treated, of typeNUMERIC, refers to theidcolumn of thepatientstable so theforeign keyconstraint is applied.doctor_id, indicates the ID of the doctor who treated the patient, is saved with theNUMERICtype, and refers to theidcolumn of thedoctorstable so theforeign keyconstraint is applied.doc_assistant_id, indicates the ID of the dental assistant who helped the doctor during the treatment asNUMERIC, refers to theidcolumn of theassistantstable so theforeign keyconstraint is applied.treatment_id, indicates the ID of the treatment that was given to the patient. It refers to theidcolumn of thetreatmentstable so theforeign keyconstraint is applied.referred_to, in the event that the patient requires a different treatment than the one applied and/or with a different specialization, this column will indicate the ID of the doctor to whom this patient was referred, it is of typeNUMERICand refers to theidcolumn of thedoctorstable so theforeign keyconstraint is applied.emergency, this column has theCHECKconstraint applied, if the patient was treated as an emergency “yes” is recorded, but if instead the patient was treated for a previously scheduled appointment “no” is recorded. This value is required so theNOT NULLconstraint is also applied. It is of typeTEXT.observations, if it is necessary to add a comment regarding the treatment that was performed on the patient or any event during the consultation, it will be recorded in this column, of typeTEXT.
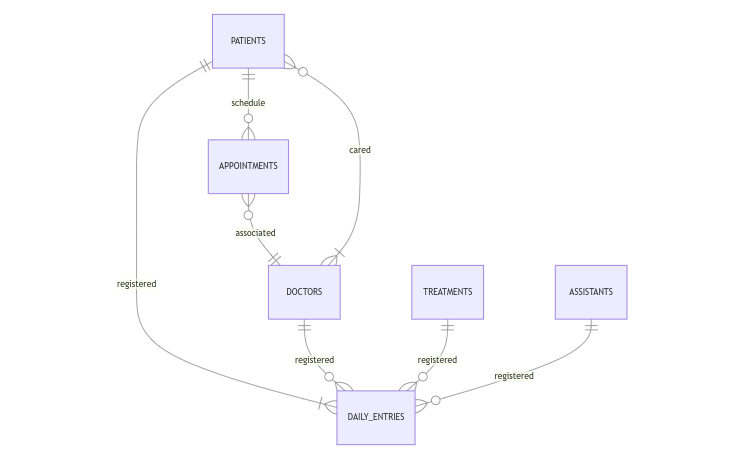
In the diagram we can see the following relationships:
- A patient can be seen by 1 or many doctors in the clinic, 1 if he/she only visited the clinic once, or many if he/she required to be treated by doctors of different specialties or perhaps the same specialty but different doctors within the same specialty. In turn, a doctor can see 0 to many patients, 0 in the case of being for example a new doctor who has not yet seen his first patient, or many if he is a doctor who has been working with the clinic for a long time.
- A patient can schedule 0 to many appointments, 0 in the case of a patient who was seen in an emergency, in this case, an emergency does not give room for a previous appointment so the patient would be registered in the table of
patientsanddaily_entriesbut not in theappointmentstable, and many if the patient needs to be seen multiple times. - Each appointment can only be associated with one and only one doctor. A doctor can be associated with 0 or many appointments, 0 if he/she is a new doctor who has not yet had his/her first patient and many if he/she is a doctor who has been working in the clinic for a long time seeing many patients.
- For a person to appear in the
patientstable he/she must have at least one entry registered in thedaily_entriestable or many entries. And each entry registered indaily_entriesmust be associated with one and only one patient. - Each entry in
daily_entriesmust record one and only one doctor. On the other hand, a doctor can be associated with several entries. - Each entry in
daily_entriesmust record one and only one treatment (in the case that the patient has undergone different treatments during the same consultation, an entry will be recorded for each treatment). A treatment can appear in none or many entries. - Each entry in
daily_entriesmust record one and only one assistant. On the other hand, an assistant can be associated with several entries.
The appointments table only shows IDs of doctors and patients, so it can be quite common to have to relate several tables to get the names of doctors and patients associated with those appointments. For this reason, a view was created that shows the dates of each appointment already with the full name of the doctor and patient. The view can then be filtered by dates according to what is needed.
In the same sense, it can also be a regular practice to search for the patients that a specific doctor has treated, or the treatments that a patient has received, or to see which doctor attended a certain emergency, to optimize this process indexes were created with the names of doctors and patients and their IDs.
This database does not take into consideration previous medical history records such as family history, surgical history, previous medical treatments, etc., nor does it record the patient's diagnosis.