This repository provides a number of alternative Microsoft (NASCOM) Basic implementations specifically for variants of the RC2014 Mini, Micro, and Classic retro-computers.
Support is provided for the following hardware options.
- RC2014 Mini, Micro, and Classic versions, with 32k of RAM.
- RC2014 Classic and Plus using 56kB of RAM (with the 64kB RAM Module).
- RC2014 Mini, Micro, and Classic using the Am9511A APU Module.
- RC2014 Classic and Plus using the 8085 CPU Module.
- RC2014 Classic and Plus using the 8085 CPU Module and the Am9511A APU Module.
The code is originally derived from the NASCOM implementation of Microsoft Basic 4.7, and was adapted for the Simple Z80 by Grant Searle. Further adaptions here have focused on bug fixes, and functional and performance improvements.
The key differences over previous implementations include.
- The serial interface is configured for 115200 baud with 8n2 setting and RTS hardware handshake.
- A serial and memory sanity self check is undertaken on startup, to ensure that I/O and RAM are available and are working.
- ACIA 6850 interrupt driven serial I/O supporting the hardware double buffer, together with a large receive buffer of 255 bytes, to allow efficient pasting of Basic into the editor. The receive RTS handshake shows full before the buffer is totally filled to allow run-on from the sender.
- Interrupt driven serial transmission, with a 63 byte buffer, to ensure the CPU is not held waiting during transmission.
- A
RST,INT0, andNMIRAM redirection jump table, starting in RAM at0x8000, enables the important RST instructions and interrupt vectors to be reconfigured by the user. - These ROMs provides both an Intel HEX
HLOADstatement and softwareRESETstatement. This allows you to easily upload Z80 (or 8085) assembly or compiled C programs, and then run them as described. TheHLOADstatement automatically adjusts the upper RAM limit for Basic and enters the program origin into theUSRLOClocation. - Added
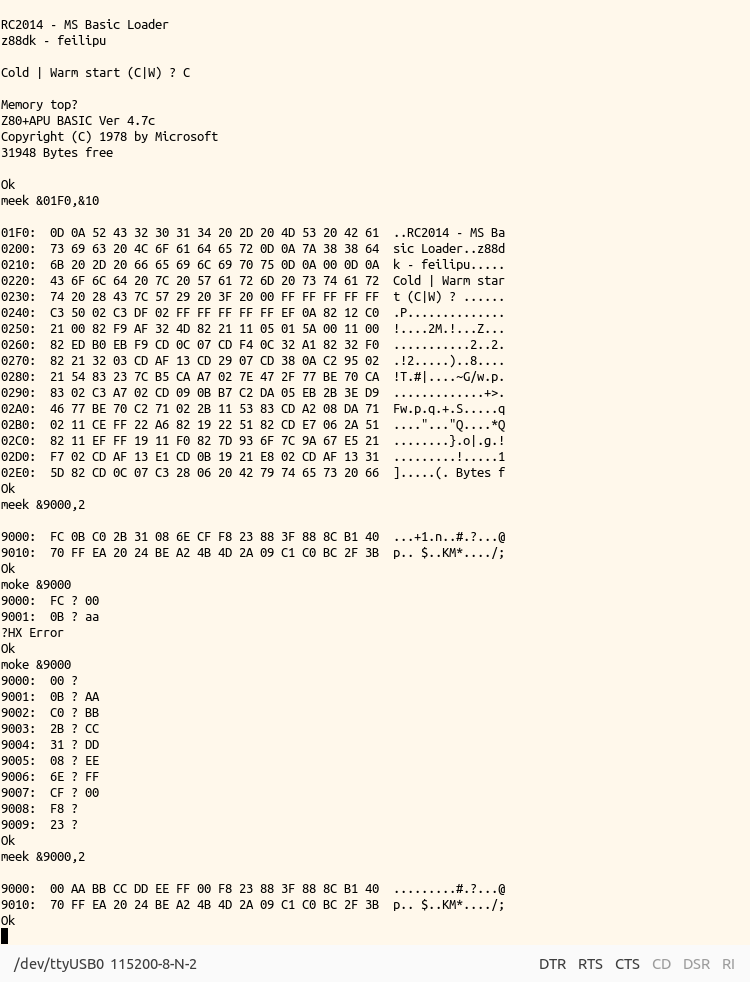
MEEKandMOKEstatements allow bulk memory to be examined in 16 byte blocks, and support continuous editing (assembly language entry) of memory. Addresses and values can be entered as signed decimal integers, or as hexadecimal numbers using the&keyword. - The standard
WIDTHcommand has been extended to support setting the comma column screen width usingWIDTH I,JwhereIis the screen width andJis the comma column screen width. - Instruction and code flow tuning result in faster execution.
- Support for the Am9511A APU Module provides a 3x to 5x faster execution of assembly or C floating point programs.
This ROM works with the Mini, Micro, and Classic versions of the RC2014, with 32k of RAM.
This is the ROM to choose if you want fast I/O from a standard RC2014, together with the capability to upload and run C or assembly programs from within MS Basic. This ROM provides both the HLOAD, RESET, MEEK, MOKE statements, and a RST, INT0, and NMI RAM Jump Table, starting at 0x8000. This allows you to upload Assembly or compiled C programs, and then run them as described.
This version works with the Classic or Plus version of the RC2014 running with a 64k/56k RAM Module. The 56k version utilises the full 56k memory space of the RC2014, with RAM starting at 0x2000.
This ROM works with the Mini, Micro, and Classic versions of the RC2014, with 32k of RAM, if you have installed an Am9511A APU Module.
This ROM works with the Classic or Plus version of the RC2014, with 32k of RAM, running with an 8085 CPU Module. This is the ROM to choose if you have installed an 8085 CPU Module.
This version works with the Classic or Plus version of the RC2014, with 32k of RAM, running with an 8085 CPU Module and an Am9511A APU Module. This is the ROM to choose if you have installed both an 8085 CPU Module and an Am9511A APU Module.
There are a number of important Z80 addresses or origins that can be adjusted and managed if you are writing an assembly or C program.
For convenience, because we can't easily change the ROM code interrupt routines already present in the RC2014, the ACIA serial Tx and Rx routines are reachable by calling RST instructions from your program.
- Tx:
RST 08Hexpects a byte to transmit in thearegister. - Rx:
RST 10Hreturns a received byte in thearegister, and will block (loop) until it has a byte to return. - Rx Check:
RST 18Hwill immediately return the number of bytes in the Rx buffer (0 if buffer empty) in thearegister. - ACIA Interrupt:
RST 38His used by the ACIA 68B50 Serial Device (8085 CPU Module systems use IRQ 6.5).
All RST xxH targets can be rewritten in a JP table originating at 0x8000 in RAM. This allows the use of debugging tools and reorganising the efficient RST call instructions as needed.
The NASCOM Basic Manual Appendix D describes the use of the USR(x) function to call assembly (or compiled C) programs directly from the Basic command line or from within a Basic program. Please refer to the Manual Appendix D for further information on mixing Basic and Assembly code.
For the RC2014 with 32k Basic the location for the USRLOC user program address is 0x8204, and with 56k Basic the location for USRLOC is 0x2204.
The MEEK I,J and MOKE I statements can be used to hand edit assembly programs, where I is the address of interest as a signed integer, and J is the number of 16 byte blocks to display. MOKE byte entry can be skipped with carriage return, and is exited with CTRL C. For hand assembly programs the user program address needs to be manually entered into the USRLOC address 0x8204 using DOKE.
Address entry can also be converted from HEX to signed integer using the & HEX prefix, i.e. in MOKE &9000 0x9000 is converted to −28672 which is simpler than calculating this signed 16 bit integer by hand, and MEEK &2000,&10 will tabulate and print 16 blocks of 16 bytes of memory from memory address 0x2000.
-
Select the preferred origin
ORGfor your arbitrary program, and prepare an Intel HEX file from your program using your preferred assembler, or compile a C program using z88dk. For RC2014 Basic 32kB, suitable origins commence from0x8400, and the default z88dk origin for the RC2014 target is0x9000. For RC2014 Basic 56kB, suitable origins commence from0x2400. -
Give the
HLOADcommand within Basic. -
Using a serial terminal, upload the HEX file for your arbitrary program that you prepared in Step 1, using the Linux
catutility or similar. If desired the pythonslowprint.pyprogram can also be used for this purpose.python slowprint.py > /dev/ttyUSB0 < myprogram.hexorcat > /dev/ttyUSB0 < myprogram.hex. The RC2014 interface can absorb full rate uploads, so usingslowprint.pyis an unnecessary precaution. -
Start your program by typing
PRINT USR(0), or?USR(0), or other variant if you have a parameter to pass to your program. The program should return to Basic on completion.
Note that your program and the USRLOC jump address setting will remain in place through a RC2014 Warm Reset, provided you prevent Basic from initialising the RAM locations you have used. Also, you can reload your assembly program to the same RAM location through multiple Warm Resets, without issuing a RESET statement.
Any Basic programs loaded will also remain in place during a Warm Reset.
Issuing the RESET statement will clear the RC2014 RAM, and return the original memory contents equivalent to a cold start.
There are several Intel HEX versions of the Zen assembler with different RAM origins prepared to use from within RC2014 NASCOM Basic. Use the HLOAD Basic statement to load your choice of HEX file based on how much RAM you wish to leave available for Basic, and launch Zen with ?USR(0). Exit back to MS Basic with Q.
Use the Zen ORG and LOAD statements to place assembled programs above the Zen EOFP. Use Zen H to determine where EOFP is located. On return to Basic, assembled programs can be launched using the ?USR(0) command either from immediate mode, or from within a Basic program, after setting the correct USRLOC location.
Check the NASCOM Basic Manual Appendix D for further information on mixing Basic and Assembly code.
MS Basic uses 4 byte values extensively as floating point numbers in Microsoft Binary Format, and as pointers to strings. Many of the improvements are in handling these values as they are shifted around in memory, and to BCDE registers and the stack.
- 4
LDIinstructions are used to move values from one location (the Floating Point RegisterFPREG) to another location in memory, and these are in-lined to also save the call-return cycles. - The
LD (x),DELD(x+2),BCinstruction pair is used to grab values into registers and save from registers, avoiding the need to preserveHLand often saving push-pop cycles and of course the call-return cycles. - There is a 16_16x16 multiply
MLDEBCused to calculate table offsets, which was optimised to use shift instructions available to the Z80. I experimented with different zero multiplier checks, and with removing the checks, but Microsoft had already done the right optimisation there, so it was left as it was. - The extensions that Grant Searle had inserted into the operand evaluation chain to check for Hex and Binary numbers were moved to the end of the operand checks, so as not to slow down the normal operand or function evaluation. Code flow for Hex support was simplified and more fully integrated.
Doing these changes got about 6% improvement in the benchmarks.
The next step was to use the z88dk-ticks tool to evaluate hotspots and try to remediate them. Using the debug mode it is possible to capture exactly how many iterations (visits) and how many cycles are consumed by each instruction.
The testing revealed that the comparison function CPDEHL was very heavily used. As it is quite small, and through removing the call-return overhead, it adds only a few bytes per instance to in-line it. There is plenty of space in the 8kB ROM to allow this change so it was made.
Then, the paths taken by the JR and JP conditional instructions were examined, by checking which path was taken most frequently across the benchmarks. This resulted in changing a few JR instructions for JP instructions, when the conditional path was mostly true, and one replacement of a JP instruction where the conditional was most often false.
Looking further at z88dk-ticks hotspot results, the next most used function is GETCHR used to collect input from code strings. GETCHR is a larger function and is used about 50 times throughout the code base, so there is little point to in-line it. However I do note the new JR conditional is used in checking for spaces in token strings, which does save a few cycles. Microsoft warns in the Nascom Basic Manual to optimise performance by removing spaces in code. Now it is even more true than before.
As the Z80 and 8085 have better shift instructions than the 8080, these instructions have been used where possible. Specifically for the 8085 the rl de and the sra hl undocumented instructions have been used where appropriate.
So with these changes we are now at 12% improvement over the original Microsoft code.
EDIT the CPDEHL inline optimisation was reverted to provide space to add the MEEK and MOKE statements, so we're back to 9% improvement.
So at this point I'll call it done. It seems that without rewriting the code substantially that's about all that I can squeeze out. The result is that with no change in function, MS Basic for Z80 is now simply 9% faster.
YAZ180 (deprecated, see yabios)
ASCI0 interrupt driven serial I/O to run modified NASCOM Basic 4.7.
If you're using the YAZ180 with 32kB Nascom Basic, then all of the RAM between 0x3000 and 0x7FFF is available for your assembly programs, without limitation. In the YAZ180 the area between 0x2000 and 0x2FFF is reserved for system calls, buffers, and stack space. For the RC2014 the area from 0x8000 is reserved for these uses.
In the YAZ180 32kB Basic, the area from 0x4000 to 0x7FFF is the Banked memory area, and this RAM can be managed by the HexLoadr program to write to all of the physical RAM space using ESA Records.
HexLoadr supports the Extended Segment Address Record Type, and will store the MSB of the ESA in the Z180 BBR Register. The LSB of the ESA is silently abandoned. When HexLoadr terminates the BBR is returned to the original value.
Two versions of initialisation routines NASCOM Basic are provided.
The 56k version utilises the full 56k RAM memory space of the YAZ180, starting at 0x2000.
Full input and output ASCI0 buffering. Transmit and receive are interrupt driven.
Receive buffer is 255 bytes, to allow efficient pasting of Basic into the editor. Receive buffer overflows are silently discarded.
Transmit buffer is 255 bytes, because the YAZ180 is 36.864MHz CPU. Transmit function busy waits when buffer is full. No Tx characters lost.
The 32k version uses the CA0 space for buffers and the CA1 space for Basic.
This leaves the Bank RAM / Flash space in 0x4000 to 0x7FFF available for other usage.
The rationale is to allow in-circuit programming, and an exit to another system. An integrated HexLoadr program is provided for this purpose.
Full input and output ASCI0 buffering. Transmit and receive are interrupt driven.
Receive buffer is 255 bytes, to allow efficient pasting of Basic into the editor. Receive buffer overflows are silently discarded.
Transmit buffer is 255 bytes, because the YAZ180 is 36.864MHz CPU. Transmit function busy waits when buffer is full. No Tx characters lost.
https://feilipu.me/2016/05/23/another-z80-project/
NASCOM ROM BASIC Ver 4.7, (C) 1978 Microsoft
Scanned from source published in 80-BUS NEWS from Vol 2, Issue 3 (May-June 1983) to Vol 3, Issue 3 (May-June 1984). Adapted for the freeware Zilog Macro Assembler 2.10 to produce the original ROM code (checksum A934H).
http://www.nascomhomepage.com/
The HEX number handling updates to the original NASCOM BASIC within this file are copyright (C) Grant Searle
You have permission to use this for NON COMMERCIAL USE ONLY. If you wish to use it elsewhere, please include an acknowledgement to myself.
The rework to support MS Basic MEEK, MOKE, HLOAD, RESET, and the 8085 and Z80 instruction tuning are copyright (C) 2020-2023 Phillip Stevens
This Source Code Form is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License, v. 2.0. If a copy of the MPL was not distributed with this file, You can obtain one at http://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/.
@feilipu, August 2020