Mashr is an easy-to-use data pipeline orchestration and monitoring framework for small applications. Mashr simplifies the process of taking your data from disparate sources and putting them into a single place so that you can use that data. It is optimized for data pipeline best practices including monitoring for each step of your data pipeline along with archiving and backup in case of failover. Mashr is built with Node.js, provides an easy-to-use CLI, and uses Docker to host Embulk on GCE Instances on Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Read our case study to learn more about how we built Mashr.
Jacob Coker-Dukowitz Software Engineer San Francisco, CA
Linus Phan Software Engineer Los Angeles, CA
Mat Sachs Software Engineer Portland, OR
- GCP (Google Cloud Platform) account
- GCP project, service account email, and json keyfile
- GCP Cloud SDK
- Node.js >= 8
- NPM
Mashr requires that users have a project with a service account on GCP and set up the Cloud SDK CLI on their local machine. If you have not already done so, please Download the Cloud SDK and use the "console" to create a project and a service account with a role of "owner". Mashr will use the project id, service account email, and service account json keyfile to to interact with GCP services.
npm install -g mashr
- Make sure you have a Google Cloud Platform (GCP) account
- Create a new project in your Google Cloud account
- After creating a new project, you will need to enable the Cloud Functions
API from the web console.
- Go to the main menu and choose "APIs & Services"
- Click the "+ Enable APIs and Services" button at the top of the page
- Search for "Cloud Function" (no 's')
- Click "Cloud Functions API"
- Click "enable" to enable the API
Mashr was made to be an easy-to-use framework with just a few commands so that developers can get started quickly building their own data pipelines. Below are the main commands with a brief description:
init- creates a YAML configuration file in the user's working directorydeploy- launches all of the GCP resources to create the data pipelinedestroy- destroys all of the GCP resources of a specific data pipelinelist- lists your current data pipelineshelp- help text for Mashr
First, you would run mashr init which sets up the user’s current working directory as a mashr directory. It would create a mashr_config.yml file in the user’s current working directory. The user then fills out the mashr_config.yml file to tell Mashr what data source it will be pulling from and what BigQuery dataset and table the data should go to.
After completing the mashr_config.yml file you run mashr deploy. This will create a data pipeline with monitoring, failover and archiving in your GCP account.
Read the case study to learn about what resources are created and why.
mashr init [--template <template_name>]
Initializes your current working directory with a template mashr_config.yml
file necessary for running mashr deploy. Optionally include the --template
flag and name of the template. Template names currently include: http, psql,
and random.
mashr deploy
Deploys the integration: adds it to the list of mashr integrations and creates related GCP resources including staging and archive GCS buckets, a cloud function and a GCE instance.
Creates a 'function' folder that stores the code the Cloud Function uses in
this integration. You can edit and redeploy the Cloud Function with gcloud.
You can edit and redeploy the Cloud Function with gcloud using this command,
where the integration_name from mashr_config.yml is the name of your function
and bucket:
gcloud functions deploy <FUNCTION_NAME> \
--runtime nodejs8 \
--trigger-resource <BUCKET_NAME> \
--trigger-event google.storage.object.finalize
mashr list
Lists all integrations that the user has deployed.
mashr destroy <integration name>
Destroys the integration: removes it from the list of mashr integrations and destroys related GCP resources including the staging and archive GCS buckets, the cloud function and the GCE instance.
mashr help
Documentation of commands.
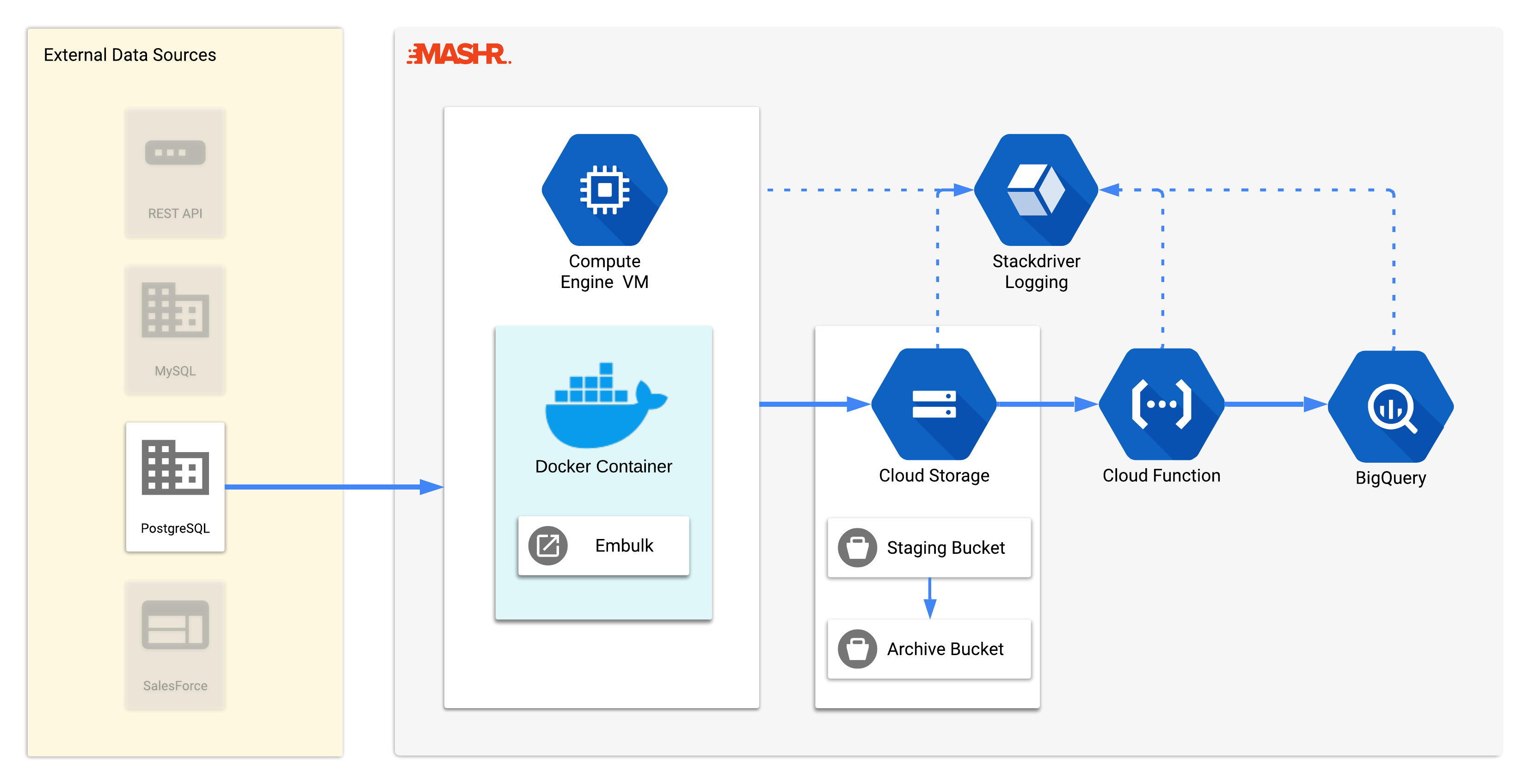
This diagram shows a high-level overview of Mashr’s main components. When you run mashr deploy in your terminal, the following actions take place:
Mashr sets up a GCE instance, with Embulk running on a Docker container. The container has a cron job running that pulls data from the source and loads it into Google Cloud Storage. Adding the data to GCS triggers the Cloud Function. The Cloud Function attempts to load the data into BigQuery. If the load is successful, the Cloud Function moves the data file from the staging bucket to the archive bucket. If the load is not successful, the data file remains in the staging bucket for debugging purposes. Each step of this process has Stackdriver monitoring enabled so users can debug the data pipeline if necessary.
Read the case study to learn more about the architecture of Mashr and the design choices we made.
Consider colocating as many as your services as possible. For example, it's required that your GCS (Google Cloud Storage) and GBQ (Google Big Query) be located in the same regions. See the Locations Considerations document for more information